CT Scanner
16 Slice CT Scanner / 3.5 MHU Tube
CT (Computed Tomography)
We are using one of the leading brand 16 Slice CT Scanner / 3.5 MHU Tube Access CT machine of Philips for CT (Computed Tomography)
As computers have become more powerful and less expensive, CT systems have become a more efficient mode of inspection technology. Coupled with the use of We are using one of the leading brand 16 Slice CT Scanner / 3.5 MHU Tube Access CT machine of Philips for CT (Computed Tomography)
As computers have become more powerful and less expensive, CT systems have become a more efficient mode of inspection technology. Coupled with the use of Flat Panel Detectors, CT systems have drastically reduced scanning and image processing times.
CT, or CAT scans, are special X-ray tests that produce cross-sectional images of the body using X-rays and a computer. CT scans are also referred to as computerized axial tomography.
CT scanners first began to be installed in 1974. CT scanners have vastly improved patient comfort because a scan can be done quickly. Improvements have led to higher-resolution images, which assist the doctor in making a diagnosis. For example, the CT scan can help doctors to visualize small nodules or tumours, which they cannot see with a plain film X-ray.
CT Scan Facts
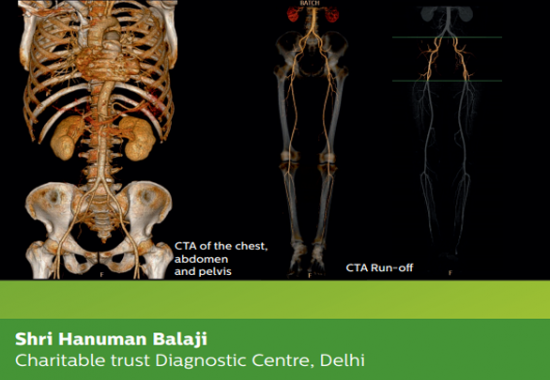
- CT scan images allow the doctor to look at the inside of the body just as one would look at the inside of a loaf of bread by slicing it. This type of special X-ray, in a sense, takes “pictures” of slices of the body so doctors can look right at the area of interest. CT scans are frequently used to evaluate the brain, neck, spine, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and sinuses.
- CT has revolutionized medicine because it allows doctors to see diseases that, in the past, could often only be found at surgery or at ⦁ autopsy. CT is non-invasive, safe, and well-tolerated. It provides a highly detailed look at many different parts of the body.
- People often have CT scans to further evaluate an abnormality seen on another test such as an X-ray or an ⦁ ultrasound. They may also have a CT to check for specific symptoms such as pain or ⦁ dizziness. People with ⦁ cancer may have a CT to evaluate the spread of disease.
- A head or brain CT is used to evaluate the various structures of the brain to look for a mass, ⦁ stroke, area of ⦁ bleeding, or blood vessel abnormality. It is also sometimes used to look at the skull.
- A neck CT checks the soft tissues of the neck and is frequently used to study a lump or mass in the neck or to look for enlarged ⦁ lymph nodes or glands.
- CT of the chest is frequently used to further study an abnormality on a plain chest X-ray. It is also often used to look for enlarged lymph nodes.
- Abdominal and pelvic CT looks at the abdominal and pelvic organs (such as the liver, spleen, kidneys, pancreas, and adrenal glands) and the gastrointestinal tract. These studies are often ordered to check for a cause of pain and sometimes to follow up on an abnormality seen on another test such as an ultrasound.
- A sinus CT exam is used to both diagnose sinus disease and to detect a narrowing or obstruction in the sinus drainage pathway.